SDK Configuration Properties
Refer various SDK config properties applicable for WebAR SDK
WebAR SDK can be configured to select the mode (surface or marker tracking), customize the logo, style of the splash screen, UI screens (shown by SDK) etc using the following SDK configuration parameters.
These parameters can be used in different ways:
Adding as properties in javascript object window.WEBAR_SDK_CONFIG. A separate script having this object defined has to be included before loading the SDK <script> tag.
Example:
webar-sdk-config.js
window.WEBAR_SDK_CONFIG = {
"webar-mode": "surface-tracking",
"rendering-engine": "playcanvas",
"auto-init": "true",
"logo-src": "../images/test_logo_here.png"
};index.html :
<script src="https://webar-sdk.blippar.com/releases/live-config/playcanvas/webar-sdk-config-surface.js"></script>
<script src="https://webar-sdk.blippar.com/releases/latest/cdn/blippar/webar-sdk-v1.2.0-beta.min.js?license-key=xxxxxxxx-1111-2222-3333-yyyyyyyyyyyy"></script>Adding as html attributes to the <script> tag in which the WebAR SDK js file is loaded.
Adding as a URL search params in the SDK script tag url.
Only the license-key property can be passed via URL search params. Passing other properties via URL will not work.
Example:
alert-background-color
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the background color of the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-border-color
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the border color of the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-border-width
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the border thickness of the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-border-radius
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the border radius of the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-button-border-radius
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the border radius of the OK button in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-box-font-size
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the font size of the text in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-box-height
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the height of the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-box-width
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the width of the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-button-color
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the button color in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-button-height
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the button height in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-button-text-color
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the button text color in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-camera-permission-button-text
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the camera permission button text in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-camera-permission-text
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the camera permission text in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-message-text-color
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the text color in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-motion-permission-button-text
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the motion sensor permission button text in the notice alert dialog.
Example
alert-motion-permission-text
Description
On iOS Safari browser, a Camera permission request notice is displayed before asking the user to allow access to the Camera. This attribute changes the motion sensor permission text in the notice alert dialog.
Example
anonymize-ip-addresses
Description
Enables anonymization of IP addresses in analytics to align with privacy regulations and user preferences.
Example
auto-init
Description
When SDK and A-Frame components with webar-* attributes are loaded, the AR experience starts automatically by default. In case the AR experience has to be started only after an event or user intervention, then auto-init attribute can be set to "false".
Example
auto-marker-detection
Description
It enables auto marker detection so that user doesn't have to manually click the scan button, rather it detects automatically when it recognises a marker.
Example
auto-scan-instruction
Description
User can change the default scan instruction for auto marker detection, i.e. when auto-marker-detection sets to 'true'.
Example
auto-scan-instruction-detect
Description
User can change the default scan instruction when marker is detecting i.e. recognises a marker image.
Example
auto-scan-instruction-idle
Description
User can change the default scan instruction when phone is idle
Example
auto-scan-instruction-idle-on-desktop
Description
User can change the default scan instruction when desktop camera view is idle i.e no valid marker is detected. If no valid marker is detected within 5 minutes, user has to reload the page to start detection to work again.
Example
auto-scan-instruction-text-style
Description
Changes the css style of scan instruction text element.
Example
auto-scan-style
Description
User can change css style of scan instruction html element.
Example
auto-scan-style-display
Description
User can change the display style of auto scan html element
Example
auto-start[deprecated]
⚠️ Deprecation Notice:
The configuration parameter auto-start has been renamed to auto-start-tracking for improved clarity. This change addresses previous ambiguity around what the SDK automatically starts—specifically clarifying that it controls auto-start behavior of AR tracking, not the entire application.
Please update your integration to use:
(Default is true. Set to false if you prefer manually starting AR tracking.)
auto-start-tracking
Description
When sdk and A-Frame components with webar-* attributes are loaded, the AR experience starts automatically by default. In case the AR experience has to be started only after an event or user intervention, then the auto-start attribute can be set to "false".
Example
desktop-logo-height / desktop-logo-width
Description
Changes the height and width of the logo image displayed in a desktop browser where the user is asked to scan the QR code or type the url in Android or iOS mobile browsers.
Example
desktop-logo-src
Description
Changes the logo image displayed in a desktop browser where the user is asked to scan the QR code or type the url in Android or iOS mobile browsers.
Example
disable-ar-facing-camera
Description
When the stage cursor feature is enabled, the AR object will automatically orient itself to face the camera each time the user taps on the surface. This behavior is controlled by the disable-ar-facing-camera setting. If this setting is false, the AR object will continue to face the camera. Conversely, if the setting is true, the AR object will not adjust its orientation to face the camera upon user interaction.
Example
disable-mirroring
Description
Disables video mirroring for Face and Marker tracking modes. By default, the camera feed is mirrored in these modes; setting this to true renders the feed exactly as captured.
Example
enable-front-camera-for-marker-tracking
Description
Enables marker tracking using the front-facing camera, allowing for selfie-style marker experiences.
Example
enable-tracking-on-desktop
Description
To enable/disable tracking on the desktop browser. This will be useful while developing the marker tracking application on the desktop itself. It also works with the developer console's mobile simulator in Chrome desktop browser.
Right now only Marker tracking is supported on the desktop browser.
When set to "false", tracking is disabled on the desktop browser and the default qr code page is seen.
When set to "true", tracking is enabled on the desktop browser and the camera view is seen.
Default value is "false".
Also by default the camera view displayed is a mirrored image of the real world. To enable/disable this mirroring see enable-mirroring-on-desktop attribute for more details.
Example
enable-mirroring-on-desktop
Description
To enable/disable mirroring of the camera view displayed on the desktop browser when enable-tracking-on-desktop is set to "true".
When set to "false", mirroring of the camera view is disabled on the desktop browser.
When set to "true", mirroring of the camera view is enabled on the desktop browser.
Default value is "true".
Example
enable-photo-ui
Description
To enable/disable displaying the default snapshot camera icon.
When set to "true", a camera icon is displayed at the bottom the screen. On clicking it, user can take a snapshot of the experience and then see the preview of the snapshot to download it.
When set to "false", camera icon is not displayed. In this case, a custom snapshot UI can be implemented using WEBARSDK.TakeSnapShot() API.
Default value is "false".
Example
external-camera-stream
Description
The external-camera-stream attribute allows developers to provide their own camera stream to the WebAR SDK instead of letting the SDK manage camera initialization internally. When enabled, the SDK will wait for an external MediaStream to be provided via the SetCameraStream() API method.This feature is particularly useful for:
Custom camera implementations with specific configurations
Integration with existing camera management systems
Advanced camera controls (resolution, frame rate, effects)
Testing scenarios with recorded video streams
Multi-camera applications where camera switching is managed externally
Custom video processing pipelines before AR tracking
Default value is "false".
Example
gesture-rotation-speed
Description
The gesture-rotation-speed attribute determines the responsiveness of the AR object's rotation to user gestures. It modulates how quickly the object turns in response to user input:
A higher value results in a more rapid rotation, allowing the object to spin faster with each swipe. This can be useful for scenarios where quick, broad movements are desired.
A lower value yields a slower, more precise rotation, granting the user finer control over the object's orientation. This setting is ideal for detailed adjustments and nuanced interactions.
Example
gesture-scale-max
Description
The gesture-scale-max attribute specifies the upper limit for the scale factor applied to an AR object when users perform pinch-to-zoom gestures. This setting controls the maximum size the AR object can reach through user interaction, effectively capping the object's enlargement to ensure it does not exceed the intended proportions within the AR scene.
By configuring the gesture-scale-max attribute, you can provide a safeguard against excessive scaling, maintaining the aesthetic and functional balance of the AR experience.
Example
gesture-scale-min
Description
The gesture-scale-min attribute sets the minimum allowable scale factor for an AR object within a single pinch gesture. It defines the least amount of scaling down that can be applied, ensuring that the object does not become too small to interact with or perceive after one pinch interaction. This constraint helps maintain the object's presence and usability within the AR scene.
Please note that this attribute accepts a value greater than 0 and less than 1, which represents the proportional size of the object relative to its initial scale. Setting it to 1 would maintain the object's original size, effectively disabling any scale-down action, as each scale-down gesture considers the object's current scale as the base factor of 1. Values less than 1 decrease the object's size proportionally, with smaller values allowing for more significant reduction.
Example
hide-reset-button
The hide-reset-button attribute allows developers to control the visibility of a reset button within the AR interface. When set to true, this attribute hides or removes the reset button from the user interface, streamlining the experience by eliminating unnecessary elements. This can be particularly useful if the reset functionality is not required or if you wish to manage state resets through custom controls or interactions.
Example
ios-camera-permission
Description
To enable/disable the camera permission alert dialog(generated by the sdk) on iPhone devices before showing the iOS system request to access the camera.
When set to "false", A Camera and Motion permission alert is shown only during the first time the application is loaded on the browser.
When set to "true", A Camera and Motion permission alert is shown during the first time the application is loaded on the browser. After that for every load, only the Camera alert is shown.
The advantage of showing the camera permission alert during every load is to start the auto playback of the video(if any) in the AR experience. In iOS Safari browser, a video cannot be played automatically when the scene is loaded. Instead it has to be played only after a user interaction. With this camera alert interaction, the app can start and pause the AR scene videos (using the callback from SetCameraAlertCallback() API) and also starts the iOS system alert to access the camera. Once the tracking has started, the paused videos can be played programatically to look like it is auto-played.
The default value of this attribute is "true".
Example
issue-img-height / issue-img-width
Description
Changes the height and width of the warning symbol image displayed in the landscape warning screen, or any device/server communication error.
Example
issue-img-src
Description
Changes the warning symbol image displayed in the landscape warning screen, or any device or server communication error.
Example
loading-progress-type
Description
Changes the loading progress bar/info type. If the value is "default", it shows the loading update in text like "Created 1 of 3 elements". It shows Blippar's default style. If the value is "circular", it shows a circular progress bar.
Example
logo-height / logo-width
Description
Changes the height and width of the circular logo in the loading splash screen.
Example
logo-src
Description
Changes the circular logo in the loading splash screen.
Example
minimal-ui
Description
The minimal-ui attribute enables a minimal user interface mode that disables most of the WebAR SDK's built-in UI components, allowing developers to create completely custom user experiences. When enabled, the SDK operates with minimal visual elements, giving developers full control over the interface design and user interactions.This feature is ideal for:
Custom branded experiences where you want full control over the UI
Integration into existing applications with established design systems
Mobile apps using WebView where native UI is preferred
Minimal performance overhead scenarios
Custom loading and error handling implementations
UI Elements Disabled
When minimal-ui="true" is set, the following UI components are disabled:
❌ Splash Screen
Default SDK loading screen with logo
Progress indicators and loading animations
Brand logos and loading text
❌ QR Code Display
Desktop QR code for mobile device pairing
QR code card in bottom-right corner
"Scan with mobile" instructions
❌ Desktop UI Elements
Full-screen desktop experience layouts
Desktop-specific logo displays
"Open on mobile" messaging
❌ Built-in Progress Tracking
Loading progress bars and spinners
Circular progress indicators
Loading percentage displays
Portrait mode enforcement (when configured)
Orientation change detection
UI Elements Preserved
✅ Orientation Handling
Camera permission dialogs (when not using custom handlers)
System error messages
Browser compatibility warnings
✅ Error Handling
The following essential elements remain enabled even in minimal UI mode:
Example
Note: For a complete implementation example of minimal-ui="true" in action, please check the Advanced Surface Tracking Integration example or head to this section as the full example is quite extensive.
on-error
Description
The on-error callback handles all errors during SDK initialization and runtime, allowing for custom error messaging and recovery flows.
Configuration
HTML Attribute
JavaScript Function Definition
Error Data Structure
Common Error Codes
CAMERA_PERMISSION_DENIED - User denied camera access
CAMERA_NOT_AVAILABLE - No camera device found
UNSUPPORTED_BROWSER - Browser lacks required features
NETWORK_ERROR - Failed to download SDK resources
DEVICE_MOTION_PERMISSION_DENIED - Motion sensors blocked (iOS)
WEBGL_NOT_SUPPORTED - WebGL not available
INITIALIZATION_FAILED - General SDK initialization failure
Implementation Example
on-load
Description
Loads a custom splash screen. To create a custom splash screen, the user should create a function and pass the function as a string to the "on-load" attribute.
Example
on-progress
Description
The on-progress attribute allows developers to implement custom progress tracking during WebAR SDK initialization. When provided, this callback automatically disables the SDK's built-in progress UI and gives you complete control over the loading experience.
Configuration
Callback Function Definition
Progress Data Structure
Automatic Behavior
When you provide the on-progress callback:
✅ Enables useCustomProgressHandler=true automatically
❌ Disables built-in progress UI (loading screens, progress bars)
✅ Preserves error handling (unless
on-erroris also provided)✅ Maintains splash screen functionality (unless using
minimal-ui)
Best Practices
Load the callback function before the SDK to ensure availability during initialization
Handle missing or incomplete progress data with fallback animations
Provide visual feedback even when SDK data is not available
Use smooth animations for better user experience
Test on different devices to ensure consistent behavior
Include completion state handling to hide loading UI appropriately
Consider accessibility with proper ARIA labels and screen reader support
progress-dot-ring-color
Description
Changes the color of the dotted loading ring which runs indefinitely until the splash screen disappears.
Example
progress-dot-ring-scale
Description
Changes the size/scale of the dotted loading ring which runs indefinitely until the splash screen disappears.
Example
progress-ring-color
Description
Changes the color of the loading progress update ring.
Example
progress-ring-line-width
Description
Changes the thickness of the loading progress update ring.
Example
progress-ring-scale
Description
Changes the size of the loading progress update ring.
Example
render-scene-on-desktop
Description
To enable/disable the rendering of the 3D scene on the desktop without any tracking.
When the value is set to "true", the 3D scene is rendered as seen by the default virtual camera on the desktop browser (without tracking).
When set to "false", the default qr code page is displayed on the desktop browser.
Default value is "false".
Example
rendering-engine
Description
Decides which rendering engine is to be used with the application
babylonjs
BabylonJS rendering engine
playcanvas
Playcanvas rendering engine
aframe
(Default) AFrame rendering engine.
By default the AFrame rendering engine is chosen by sdk even in the following cases:
If the rendering-engine attribute is not specified in the sdk script tag
If the rendering-engine attribute is specified but the value does not match the supported values
Example
scan-btn-display
Description
Changes the css display property of the scan button displayed during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking". To make it invisible set it to "none" else "block".
Example
scan-btn-height / scan-btn-width
Description
Changes the height and width of the scan button displayed during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-img-height / scan-btn-img-width
Description
Sets the height and width of the image displayed in the scan button displayed during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-img-src
Description
Sets the image of the scan button displayed during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-img-transform
Description
Sets the SVG transform property (e.g. translate(), rotate() etc.) of the image displayed in the scan button displayed during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-img-x-coordinate / scan-btn-img-y-coordinate
Description
Sets the x and y coordinates of the image displayed in the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking". The x and y position of the image is the top left position, relative to the viewport of the origin of the element i.e the scan button. Use scan-btn-img-transform attribute's translate() method to position the image to the centre.
Example
scan-btn-instruction
Description
Changes the text below the scan button displayed during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-instruction-style
Description
Changes the css style of the text below the scan button displayed during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-progress-bar-color
Description
Sets the color of the progress foreground circular bar displayed around the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-progress-bar-cx-coordinate / scan-btn-progress-bar-cy-coordinate
Description
Sets the x and y coordinates of the centre of the progress foreground circular bar displayed around the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-progress-bar-radius
Description
Sets the radius of the progress foreground circular bar displayed around the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-progress-bar-transform
Description
Sets the SVG transform property (e.g. translate(), rotate() etc.) of the progress foreground circular bar displayed around the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-progress-circle-cx-coordinate / scan-btn-progress-circle-cy-coordinate
Description
Sets the x and y coordinates of the centre point of the progress background circle displayed around the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-progress-circle-radius
Description
Sets the radius of the progress background circle displayed around the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
scan-btn-progress-circle-style
Description
Sets the SVG style of the progress background circle displayed around the scan button during marker tracking i.e. when webar-mode="marker-tracking".
Example
show-guide-view
Description
Enable or disable displaying the default Hand with phone animation guide, which instructs the user to move the phone left and right to detect a surface.
Example
show-guide-animation-url
Description
Sets the custom animation URL for hand guide animation of surface tracking. Please note that it only supports lottie animations json format.(https://lottiefiles.com)
Example
show-qr-card-on-desktop
Description
To show/hide a "Try on Mobile" button displayed on the desktop browser. On clicking this button, it shows the QR code which can be scaned from the mobile device to load the application. This can be useful when render-scene-on-desktop attribute is set to "true".
Default value is "false".
Example
static-camera
Description
By default, sdk assumes Static-Camera-With-A-Moving-Stage i.e. 'static-camera' = 'true'. However, it can be changed to Moving-Camera-With-A-Static-Stage by setting 'static-camera' = 'false'.
Example
ui-background-color
Description
Changes the background color of the loading splash screen, landscape warning screen or any device/server communication error.
Example
ui-portrait-text
Description
Replaces the default text shown in the landscape warning screen.
Example
ui-text-color
Description
Changes the text color of the landscape warning screen, or any device/server communication error.
Example
webar-mode
Description
Decides whether to run the WebAR SDK in Surface Tracking or Image/Marker Tracking mode.
surface-tracking
Runs the WebAR SDK in Surface Tracking mode. Surface Tracking is the default mode. If this attribute is not present or any other not-supported value is provided, it runs in Surface Tracking mode.
In surface tracking mode, the <a-scene webar-scene> should have one <a-entity webar-stage> element. See webar-stage (A-frame) attribute for more details.
marker-tracking
Runs the WebAR SDK in Marker Tracking mode.
face-tracking
Runs the WebAR SDK in Face Tracking mode. Supported only when rendering-engine="aframe" for now.
lazy-mode
Runs the WebAR SDK in Lazy Mode i.e. allows the user to decide at a later stage which tracking should be enabled. The user can set the respective tracking mode using functionSetWebARMode("tracking-mode"), see the example below.
Example
Without Lazy Mode
With Lazy Mode
Playcanvas Customization
For PlayCanvas customization, kindly use the following config files which can be found at playcanvas/config folder in the downloaded SDK zip file:
webar-sdk-config-surface.js
webar-sdk-config-marker.js
These files have to be modified and hosted on a separate server (say my-server.com) and the url has to be overwritten in the Playcanvas project.
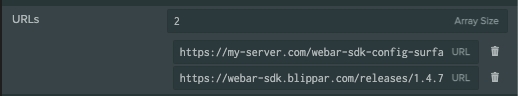
Process:
Login to Playcanvas and navigate to Settings> External Scripts > first url entry as shown below and replace the first url with your custom config url.
Last updated